Subtotal: 2.000₫
Comparision LiFePO4 vs NCM batteries
You will find on internet many articles declaring that “LiFePO4 is the safest chemistry in lithium ion battery family”, is this true or is it true in only some specific conditions? If you take a brief look on heat resistance capacity of LFP, then i can agree with you there, but this is obviously not the whole truth. When you really dig in research papers and experiments that have been conducted, you will understand that this type of chemistry has its advantages and disadvantages. How can we cater them to different applications will help to design a reliable battery system and mitigate failure risks.
Let’s journey with us for further knowledge shall we?
Can LiFEPO4 batteries catch fire or explode?
There are discussions in forums about LiFePO4 batteries doesn’t catch fire, they only emit smoke when abused.
https://powerup-technology.com/nmc-vs-lfp-safety-and-performance-in-operation/
However, there are many published scientific studies that prove that iron batteries do not just emit smoke, they catch fire and “thermal runaway” does occur. Nevertheless, temperature of the fire is not as high as that of lithium-ion NCM.
See more: LiFePO4 battery catches fire due to puncture
See more: LiFePO4 catches fire under overcharge
Comparison LiFePO4 vs NCM batteries on thermal abuse
See more: Thermal runaway là gì
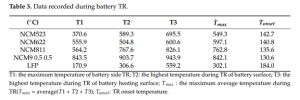
Source: MDPI
In thermal endurance testing, T -onset is the temperature at which the battery needs to heat up to start Thermal Runaway. As you can see, LFP has a much higher T-onset than other NCM batteries. This makes them more heat resistant and generally safer to handle in terms of thermal abuse.
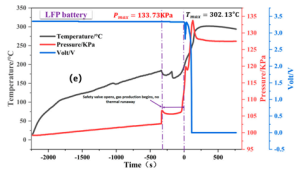 Source: MDPI
Source: MDPI
Voltage vs. temperature graph of LFP cell in thermal runaway due to thermal abuse.
Time mark “0” is when thermal runaway begins.
As shown in the figure, when heated to 184°C, the safety valve opens, gas generation process begins, but thermal runaway does not occur immediately, the voltage remains stable, and it takes 300 seconds for thermal runaway to begin.
The maximum fire temperature Tmax of LiFePO4 is 302°C, which is half of the temperature produced by NCM811. Therefore, the fire caused by NCM lithium battery is much more severe then LFP’s.
Comparison of thermal runaway phenomenon in LiFePO4 vs NCM batteries due to overcharging
Overcharging is one of the leading causes of damage to the entire battery system, and causes thermal runaway, which can cause fire or explosion, especially in electric vehicle batteries. There are three causes of this phenomenon:
(1) faulty charger or faulty BMS, and
(2) unbalanced cells in the battery pack.
Usually, the first cause will be handled by the BMS to cut off the current, but overcharging due to unbalanced cells is often overlooked, especially for LFP battery with a flat discharge curve. The cell with the higher voltage is overcharged, generating heat, heating the battery pack, causing local swelling, and finally thermal runaway is triggered. This situation is especially dangerous for batterie packs in electric vehicles, which are constructed from an outragous numbers of cells.
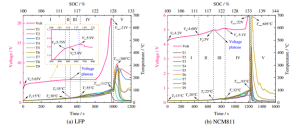
Voltage and temperature graph of LFP and NCM 40AH cells under overcharge condition
Nguồn: ScienceDirect.com
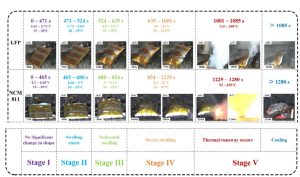
Five stages of Thermal runaway in LFP vs NCM due to overcharge. Source: ScienceDirect.com
Comparing the two graphs above, you can see the following:
The thermal runaway activation temperature in the LFP overcharge experiment was 112 °C, occurring at 1000s, while the NCM was 93 °C at 1200s. The Tmax of LFP was also ½ lower than that of NCM.
Conclusion: thermal runaway was activated earlier in LFP batteries, they also increased in temperature faster when overcharged, but the fire was not as intense as in NCM. Even in some published experiments, LFP batteries only emitted smoke but did not burn. It is remarkable to note that during thermal runaway phase, LFP did not produce O2 gas, this is due to the stable structure of (PO4) 3− on the cathode.In general, 60°C is the hot spot for overcharging experiments, where the cell begins to crack, degas, and deform due to the initiation of many exothermic reactions inside the cell.
FAQ.
Does LFP iron battery have thermal run away?
Yes.
What is the ignition temperature of LifePO4 batteries?
The highest temperature of the fire was over 308 °C.
How to put out LifePO4 battery fire?
It’s easier to put out LFP battery fire in compared to NCM’s.
Fire temperature is significantly lower with no oxygen self-generation. You use a regular fire extinguisher to cool down and isolate oxygen like an ABC extinguisher.
Does LiFePO4 battery need BMS?
YES.
LFP batteries are a branch of lithium-ion family that only operate within a certain voltage range, so it’s nescessary to have BMS to manage overcharging and discharging. This type of battery is prone to cell imbalance after long-term use, so the BMS should have a good balancing function, and the best is the BMS with bluetooth to control each cell.
What is the temperature at which thermal runaway (TR) occurs in LFP batteries?
As mentioned in the heating experiment above, the ambient temperature is 184°C for thermal runaway to occur for LFP. Compared to NCM, this figure is 90°C.
For overchange abuse, TR for LFP happens at 112 °C and NCM at 93 °C
Comparison of thermal runway risk probability of NCM with LFP.
The possibility of thermal runaway of LFP > NCM is because they tend to lose cell balance after a period of operation, they heat up quickly in a short time if electrically abused. Therefore, when using this type of battery, it is recommended that you balance the battery periodically.

 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt Update lead acid battery to lithium ion 24V 18Ah
Update lead acid battery to lithium ion 24V 18Ah 
